The universe isn’t a collection of static objects, but a vast, dynamic fabric woven with invisible movement of waves – ripples of energy that transport information, sculpt worlds, and compose the cosmic symphony.
Let’s unpack the fundamentals. A wave is a disturbance, a cosmic oscillation that propagates energy without much actual displacement of matter. They possess core characteristics:
- Wavelength (λ): The distance between crests (peaks) or troughs of a wave. This determines qualities like light’s color.
- Frequency (f): How many complete wiggles happen per second (measured in Hertz). Related to wavelength by the wave’s speed – a fundamental concept!
- Amplitude: The wave’s strength or intensity, from a gentle ripple to a mighty crash.
- Wave Speed (v): How fast the wave’s pattern travels. Depends on the wave type and the medium it moves through.

Now, let’s embark on a cosmic expedition through the marvelous diversity of waves:
Light Waves: Illuminating the Cosmos
Light, the energy that reveals the universe to our eyes, is an electromagnetic wave. Its color is simply a matter of wavelength! Long, relaxed waves paint the reds of a sunset, while zippy, short wavelengths create vibrant violets. But the electromagnetic spectrum extends far beyond the visible realm:
- Infrared (IR): The warmth of a sunny day on your skin? That’s infrared radiation in action.
- Ultraviolet (UV): Gives sunburns, helps make essential vitamins, and enables powerful sterilization processes.
- X-rays: So energetic they pass through most matter, giving us glimpses of bones or distant cosmic objects.
Other powerful players include microwaves (rotating your food and carrying distant signals), and radio waves (carrying everything from music to spacecraft communication).

Sound Waves: Symphonies of Vibrations
Unlike light, sound needs a medium – air, water, even solid ground – to travel. It’s a dance of vibrations reaching our ears!
- Pitch: Determined by frequency: fast vibrations yield high notes (a bird’s chirp), slow ones create deep sounds (a distant rumble of thunder).
- Loudness: Governed by amplitude, it’s the oomph behind a whisper versus a shout.
- Timbre: Why a violin sounds distinct from a trumpet, even on the same note. It’s the unique blend of frequencies within the wave.

Mechanical Waves: Oscillations in the World (like Earthquake!)
From guitar strings, to ripples on a pond, and even the very earth beneath your feet (earthquakes!), mechanical waves demonstrate the interconnectedness of matter:
- Transverse Waves: The oscillation is perpendicular to the wave’s motion (a vibrating string).
- Longitudinal Waves Areas of compression and expansion travel in the direction of the wave (sound in air).
- Surface Waves: Traveling where two substances meet, they shape everything from ocean waves to some seismic waves.

Because we live by a fault, this one was quite interesting! Here are more details on the above seismic waves:
P Waves (Primary Waves)
- Type: Longitudinal wave (compression and expansion in the direction of travel)
- Fastest: They travel the quickest through the Earth’s interior.
- Travel Through: Solids, liquids, and gases.
- Motion: Like a slinky being pushed and pulled.
S Waves (Secondary Waves)
- Type: Transverse wave (movement perpendicular to the direction of travel).
- Slower: Arrive after P waves.
- Travel Through: Solids only, they cannot move through liquids.
- Motion: Like a rope being shaken up and down.
Love Waves
- Type: Surface waves (travel along the Earth’s surface).
- Destructive: Cause most of the damage during earthquakes due to their horizontal shaking.
- Travel Through: Solids only.
- Motion: Side-to-side, similar to a wriggling snake.
Rayleigh Waves
- Type: Surface waves
- Rolling Motion: A combination of vertical and horizontal movement, like ocean waves.
- Travel Through: Solids only.
- Slower than Love Waves: But can also be highly destructive.
Matter Waves: The Quantum Realm Gets Funky
Buckle up, because reality is about to get delightfully weird. Even the tiniest building blocks, like electrons, exhibit wave-like behavior, a concept known as wave-particle duality. De Broglie’s relation (λ = h/p, where h is Planck’s constant and p is momentum) reveals the wavelength of these mind-bending matter waves, ushering us into the mysteries of quantum physics.

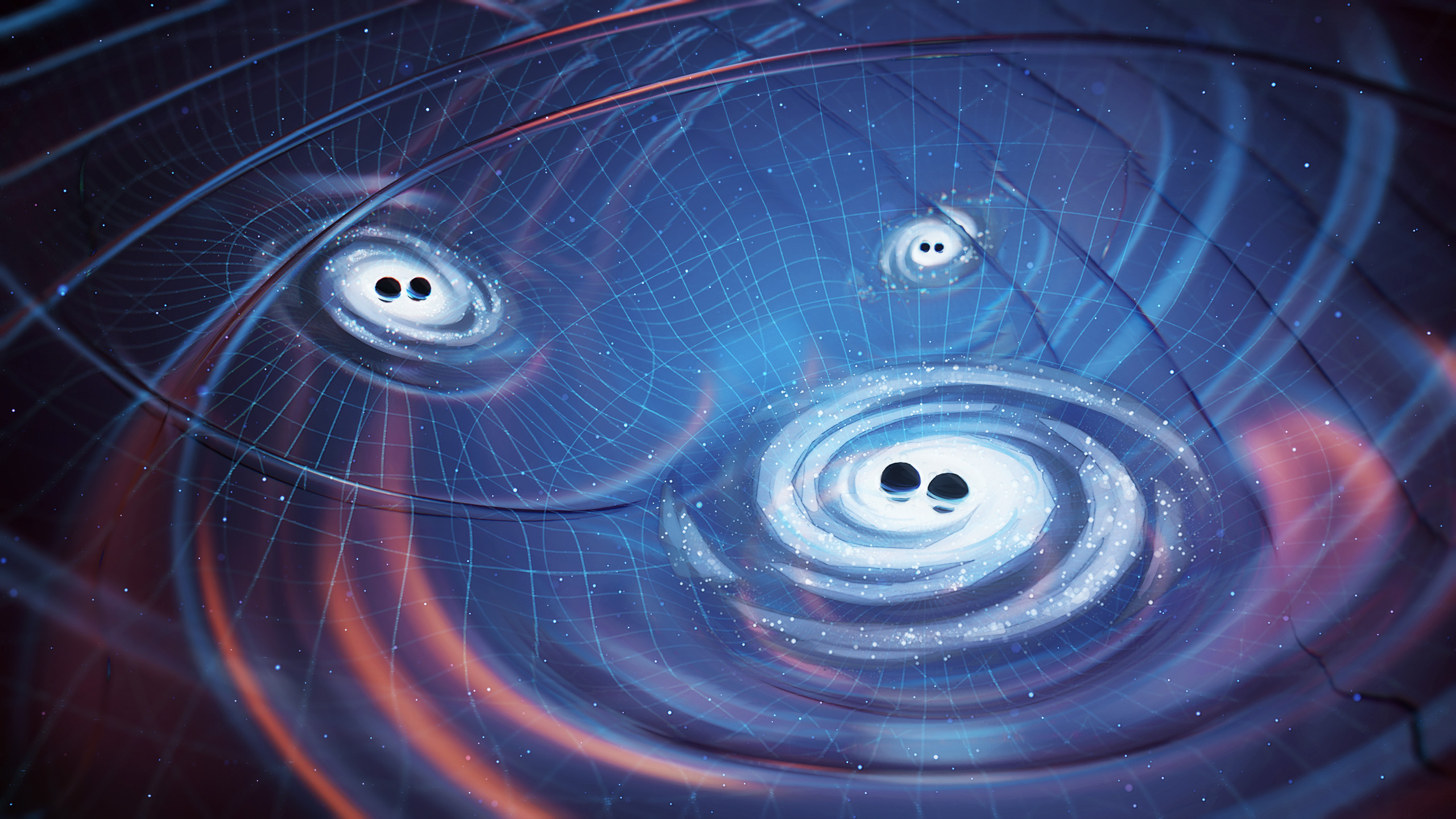
Gravitational Waves: Ripples in Spacetime
Einstein theorized these wrinkles in the very fabric of reality, ripples triggered by the universe’s most cataclysmic events. Picture black holes colliding, sending tremors across the cosmos that subtly distort space itself. Detecting them requires astonishing sensitivity (think instruments measuring changes smaller than an atom!). Gravitational waves offer an unprecedented window into the universe’s most extreme phenomena.

Waves: The Cosmic Unifier
From the gentle lapping of waves on a summer shore to the mind-bending dance of particles and colossal ripples of spacetime, waves are an essential thread in the tapestry of existence. Whether sensed by our eyes, our ears, or cutting-edge scientific instruments, they reveal a universe far more dynamic, interconnected, and awe-inspiring than we could have possibly imagined.

Comment your thoughts, interesting facts, or questions!
Trusted Tools & Services
I genuinely use these every day. If you sign up through these links, we both get a win.
Lifestyle & Ridesharing
ClassPass
Get 20 bonus credits for free (on top of the standard free trial) to try out local fitness studios and wellness spas.
Uber
Get 50% off your first 2 rides (up to $10 each). Perfect for your next trip or night out.
Lyft
Get 50% off your first 2 rides. A great alternative for reliable transportation.
Finance & Investing
M1 Finance
Get a $75 bonus when you sign up and fund a new investment account with at least $100.
Robinhood
Get a free stock (worth up to $200) just for signing up and linking your bank account.
Chase Sapphire Reserve® & Preferred®
Earn a massive sign-up bonus (75k-125k points) which can be redeemed for over $1,000 in travel through Chase Travel℠.
Chase Business Cards
Earn up to 200,000 bonus points or $1,000 cash back to jumpstart your business expenses.
Venmo
Get $5 for free after you sign up and make a qualifying payment of at least $5.
Webull
Get up to 20 free stocks when you fund your account with any amount (even just $0.01).
Coinbase & Coinbase One
Get $10 in Bitcoin after you trade $100, plus a $10 discount on your first month of Coinbase One.
Monarch Money
Get an extended 30-day free trial (instead of the usual 7) to organize and track all your financial accounts in one place.
Kalshi
Get a $25 bonus to start trading on real-world events like weather, interest rates, or elections.
MaxRewards
Supercharge your credit card rewards and perks. New users get a free month of MaxRewards Gold to automate offer activations and maximize points. Use code: lp528